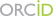Méiose et recombinaison

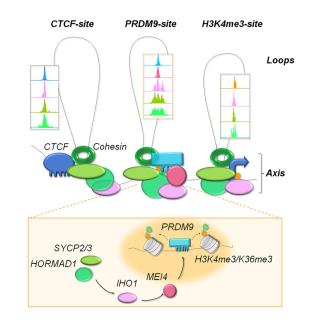
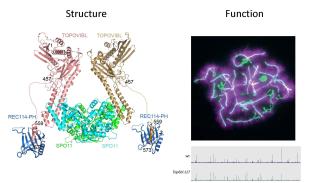
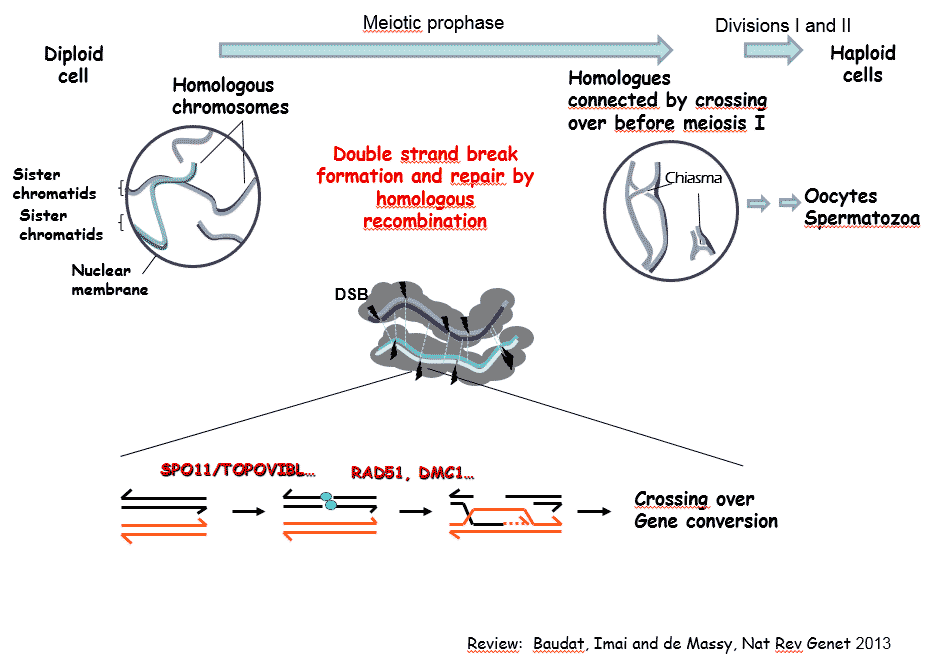
La méiose est une division cellulaire spécialisée qui permet chez les organismes à reproduction sexuée de former des cellules haploïdes à partir de cellules diploïdes. Ceci est réalisé par un cycle cellulaire constitué d’une phase de réplication de l’ADN suivi par deux divisions. La ségrégation réductionnelle des chromosomes lors de la première division de méiose nécessite l’établissement de connections entre chromosomes homologues. Celles-ci sont établies pendant la prophase de la première division par recombinaison homologue qui génère des échanges réciproques, appelés crossing over, entre homologues. L’absence de crossing over conduit le plus souvent à des défauts de ségrégation et à la stérilité. Des altérations du programme de recombinaison peuvent aussi conduire à de l’instabilité génomique et à des aneuploïdies. Par ailleurs, les événements de recombinaison homologues en méiose déterminent les associations génétiques et contribuent à la diversité des génomes et à leur évolution.
Notre equipe s’intéresse à plusieurs aspects du mécanisme moléculaire de la recombinaison méiotique et de ses implications évolutives en utilisant la souris comme système modèle. La recombinaison méiotique est initiée par l’induction programmée de centaines de cassures double brin de l’ADN dont la réparation conduit à la formation de crossing over et conversion géniques. Les principales étapes et facteurs impliqués dans ces processus ont été conservés au cours de l’évolution.
Publications de l'équipe
Principles of chromosome organization for meiotic recombination
Mathilde Biot, Attila Toth, Christine Brun, Leon Guichard, Bernard de Massy, Corinne Grey
"MeiQuant": An Integrated Tool for Analyzing Meiotic Prophase I Spread Images
Cau, J. Toe, L. D. Zainu, A. Baudat, F. Robert, T.
Mutation hotspots during meiosis
Baudat, F. de Massy, B.
Characterization of the REC114-MEI4-IHO1 complex regulating meiotic DNA double-strand break formation
Laroussi, H. Juarez-Martinez, A. B. Le Roy, A. Boeri Erba, E. Gabel, F. de Massy, B. Kadlec, J.
TOPOVIBL-REC114 interaction regulates meiotic DNA double-strand breaks
Nore A., Juarez-Martinez A. B., Clement J., Brun C., Diagouraga B., Laroussi H., Grey C., Bourbon H. M., Kadlec J., Robert T., de Massy B.
Evolution and Diversity of the TopoVI and TopoVI-like Subunits With Extensive Divergence of the TOPOVIBL subunit
Brinkmeier J., Coelho S., de Massy B., Bourbon H. M.
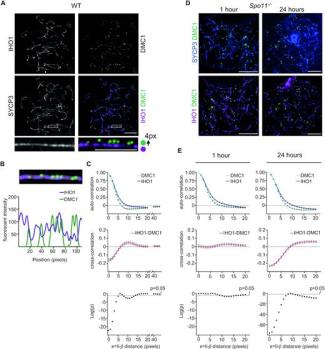
Four-pronged negative feedback of DSB machinery in meiotic DNA-break control in mice
Ihsan Dereli, Marcello Stanzione, Fabrizio Olmeda, Frantzeskos Papanikos, Marek Baumann, Sevgican Demir, Fabrizia Carofiglio, Julian Lange, Bernard de Massy, Willy M Baarends, James Turner, Steffen Rulands, Attila Tóth
Chromosome Organization in Early Meiotic Prophase.
Grey C, de Massy B
Transcriptome and translatome co-evolution in mammals
Zhong-Yi Wang, Evgeny Leushkin, Angélica Liechti, Svetlana Ovchinnikova, Katharina Mößinger, Thoomke Brüning, Coralie Rummel, Frank Grützner, Margarida Cardoso-Moreira, Peggy Janich, David Gatfield, Boubou Diagouraga, Bernard de Massy, Mark E. Gill, Antoine H. F. M. Peters, Simon Anders & Henrik Kaessmann
PRDM9 activity depends on HELLS and promotes local 5-hydroxymethylcytosine enrichment.
Imai Y, Biot M, Clément J, Teragaki M, Urbach S, Robert T, Baudat F, Grey C, de Massy B
Reading the epigenetic code for exchanging DNA.
Biot M, de Massy B
Mouse ANKRD31 Regulates Spatiotemporal Patterning of Meiotic Recombination Initiation and Ensures Recombination between X and Y Sex Chromosomes.
Papanikos F, Clément JAJ, Testa E, Ravindranathan R, Grey C, Dereli I, Bondarieva A, Valerio-Cabrera S, Stanzione M, Schleiffer A, Jansa P, Lustyk D, Fei JF, Adams IR, Forejt J, Barchi M, de Massy B, Toth A
Sex chromosome quadrivalents in oocytes of the African pygmy mouse Mus minutoides that harbors non-conventional sex chromosomes.
Baudat F, de Massy B, Veyrunes F
Mouse REC114 is essential for meiotic DNA double-strand break formation and forms a complex with MEI4.
Kumar R, Oliver C, Brun C, Juarez-Martinez AB, Tarabay Y, Kadlec J, de Massy B
PRDM9, a driver of the genetic map.
Grey C, Baudat F, de Massy B

PRDM9 Methyltransferase Activity Is Essential for Meiotic DNA Double-Strand Break Formation at Its Binding Sites.
Diagouraga B, Clément JAJ, Duret L, Kadlec J, de Massy B, Baudat F
Birth and death of a protein
Clément J, de Massy B
TopoVIL : a molecular scissor essential for reproduction
Robert, T, De Massy, B, Grelon, M.
The PRDM9 KRAB domain is required for meiosis and involved in protein interactions
Imai Y, Baudat F, Taillepierre M, Stanzione M, Toth A, de Massy B.
In vivo binding of PRDM9 reveals interactions with noncanonical genomic sites
Grey C, Clément JA, Buard J, Leblanc B, Gut I, Gut M, Duret L, de Massy B.
Meiotic DNA break formation requires the unsynapsed chromosome axis-binding protein IHO1 (CCDC36) in mice
Stanzione M, Baumann M, Papanikos F, Dereli I, Lange J, Ramlal A, Tränkner D, Shibuya H, de Massy B, Watanabe Y, Jasin M, Keeney S, Tóth A
A new light on the meiotic DSB catalytic complex
Robert T, Vrielynck N, Mézard C, de Massy B, Grelon M
The TopoVIB-Like protein family is required for meiotic DNA double-strand break formation
Robert T, Nore A, Brun C, Maffre C, Crimi B, Bourbon HM, de Massy B
SKAP, an outer kinetochore protein, is required for mouse germ cell development
Grey C, Espeut J, Ametsitsi R, Kumar R, Luksza M, Brun C, Verlhac MH, Suja JÁ, de Massy B
A Testis-Specific Chaperone and the Chromatin Remodeler ISWI Mediate Repackaging of the Paternal Genome
Doyen CM1, Chalkley GE1, Voets O1, Bezstarosti K2, Demmers JA2, Moshkin YM1, Verrijzer CP3.
Meiosis: early DNA double-strand breaks pave the way for inter-homolog repair
Borde V, de Massy B
MEI4: a central player in the regulation of meiotic DNA double strand break formation in the mouse
Kumar R, Ghyselinck N, Ishiguro KI, Watanabe Y, Kouznetsova A, Höög C, Strong E, Schimenti J, Daniel K, Toth A, de Massy B.
Anatomical and Molecular Analyses of XY Ovaries from the African Pygmy Mouse Mus minutoides
Rahmoun M, Perez J, Saunders PA, Boizet-Bonhoure B, Wilhelm D, Poulat F, Veyrunes F.
+
Développement et Pathologie de la Gonade
Human genetics. Hidden features of human hotspots
de Massy B.
Mouse tetrad analysis provides insights into recombination mechanisms and hotspot evolutionary dynamics
Cole F, Baudat F, Grey C, Keeney S, de Massy B, Jasin M.
Diversity of Prdm9 Zinc Finger Array in Wild Mice Unravels New Facets of the Evolutionary Turnover of this Coding Minisatellite
Buard J, Rivals E, Dunoyer de Segonzac D, Garres C, Caminade P, de Massy B, Boursot P.
Maraviroc-induced decrease in circulating bacterial products is not linked to an increase in immune activation in HIV-infected individuals.
Psomas C, Lavigne JP, Barbuat C, Trabelsi S, Ghosn J, Lascoux-Combe C, Flandre P, Cuzin L, Reynes J, Autran B, Corbeau P.
+
Domiciliation, activation immunitaire et infection
Meiotic recombination in mammals: localization and regulation
Baudat F, Imai Y, de Massy B.
Molecular Basis for the Regulation of the H3K4 Methyltransferase Activity of PRDM9.
Wu H, Mathioudakis N, Diagouraga B, Dong A, Dombrovski L, Baudat F, Cusack S, de Massy B, Kadlec J.
Initation of Meiotic Recombination: How and Where? Conversation and Specificities Among Eukaryotes.
De massy, B.
Cellular Source and Mechanisms of High Transcriptome Complexity in the Mammalian Testis
Soumillon M, Necsulea A, Weier M, Brawand D, Zhang X, Gu H, Barthès P, Kokkinaki M, Nef S, Gnirke A, Dym M, de Massy B, Mikkelsen TS, Kaessmann H.
SPO11-Independent DNA Repair Foci and Their Role in Meiotic Silencing
Carofiglio F, Inagaki A, de Vries S, Wassenaar E, Schoenmakers S, Vermeulen C, van Cappellen WA, Sleddens-Linkels E, Grootegoed JA, Te Riele HP, de Massy B, Baarends WM.
Dissecting the Structure and Mechanism of a Complex Duplication-Triplication Rearrangement in the DMD Gene
Ishmukhametova A, Chen JM, Bernard R, de Massy B, Baudat F, Boyer A, Méchin D, Thorel D, Chabrol B, Vincent MC, Van Kien PK, Claustres M, Tuffery-Giraud S.
Drosophila Yemanuclein and HIRA Cooperate for De Novo Assembly of H3.3-Containing Nucleosomes in the Male Pronucleus
Orsi GA, Algazeery A, Meyer RE, Capri M, Sapey-Triomphe LM, Horard B, Gruffat H, Couble P, Aït-Ahmed O, Loppin B.
RNF212 is a dosage-sensitive regulator of crossing-over during mammalian meiosis
Reynolds A, Qiao H, Yang Y, Chen JK, Jackson N, Biswas K, Holloway JK, Baudat F, de Massy B, Wang J, Höög C, Cohen PE, Hunter N.
Programmed induction of DNA double strand breaks during meiosis: setting up communication between DNA and the chromosome structure.
Borde V, de Massy B.
Spp1 links sites of meiotic DNA double-strand breaks to chromosome axes
De Massy, B.
MCM8- and MCM9-Deficient Mice Reveal Gametogenesis Defects and Genome Instability Due to Impaired Homologous Recombination
Lutzmann M, Grey C, Traver S, Ganier O, Maya-Mendoza A, Ranisavljevic N, Bernex F, Nishiyama A, Montel N, Gavois E, Forichon L, de Massy B, Méchali M.
+
Réplication et Dynamique du Génome
The Glucocorticoid-Induced Leucine Zipper (GILZ) Is Essential for Spermatogonial Survival and Spermatogenesis
Romero Y, Vuandaba M, Suarez P, Grey C, Calvel P, Conne B, Pearce D, de Massy B, Hummler E, Nef S.
Interallelic and intergenic incompatibilities of the prdm9 (hst1) gene in mouse hybrid sterility
Flachs P, Mihola O, Simeček P, Gregorová S, Schimenti JC, Matsui Y, Baudat F, de Massy B, Piálek J, Forejt J, Trachtulec Z.
What determines the localisation of spots of meiotic recombination?
Baudat F, Buard J, Grey C, de Massy B.
Mouse PRDM9 DNA-Binding Specificity Determines Sites of Histone H3 Lysine 4 Trimethylation for Initiation of Meiotic Recombination.
Grey C, Barthès P, Chauveau-Le Friec G, Langa F, Baudat F, de Massy B.
Dicer1 depletion in male germ cells leads to infertility due to cumulative meiotic and spermiogenic defects.
Romero Y, Meikar O, Papaioannou MD, Conne B, Grey C, Weier M, Pralong F, De Massy B, Kaessmann H, Vassalli JD, Kotaja N, Nef S.
The Impressionistic Landscape of Meiotic Recombination
Lichten, M., de Massy, B.
What defines the genetic map? The specification of meiotic recombination sites.
Grey C, Sommermeyer V, Borde V, de Massy B
The Molecular Chaperone Hsp90α Is Required for Meiotic Progression of Spermatocytes beyond Pachytene in the Mouse
Grad I, Cederroth CR, Walicki J, Grey C, Barluenga S, Winssinger N, De Massy B, Nef S, Picard D
A single mutation results in diploid gamete formation and parthenogenesis in a Drosophila yemanuclein-alpha meiosis I defective mutant
Meyer, RE., Delaage, M., Rosset, R., Capri, M., Ait-Ahmed, O.
Prdm9, a key control of mammalian recombination hotspots
Baudat F, Buard J, Grey C, de Massy B.
Functional conservation of Mei4 for meiotic DNA double-strand break formation from yeasts to mice
Kumar, R., Bourbon, H.M., De Massy, B.
PRDM9 Is a Major Determinant of Meiotic Recombination Hotspots in Humans and Mice
Baudat, F., Buard, J., Grey, C., Fledel-Alon, A., Ober, C., Przeworski, M., Coop, G., de Massy, B.
Distinct histone modifications define initiation and repair of meiotic recombination in mouse
Buard, J., Barthès, P., Grey, C. and de Massy, B_.
Mutation of the mouse Syce1 gene disrupts synapsis and suggests a link between synaptonemal complex structural components and DNA repair.
Bolcun-Filas, E., Speed, R., Taggart, M., Grey, C., de Massy, B., Benavente, R., Cooke, HJ.
Genome-Wide Control of the Distribution of Meiotic Recombination.
Grey C, Baudat F, de Massy B.
Parallel detection of crossovers and non-crossovers in mouse germ cells.
Baudat, F. and de Massy, B.
Distinct Functions of MLH3 at Recombination Hot Spots in the Mouse.
Svetlanov A, Baudat F, Cohen PE, de Massy B.
Repeat Length and RNA Expression Level Are Not Primary Determinants in CUG Expansion Toxicity in Drosophila Models
Le Mée, G., Ezzeddine, N., Capri, M., Aït-Ahmed, O.
Regulating double-stranded DNA break repair towards crossover or non-crossover during mammalian meiosis
Baudat, F., de Massy, B.
Cis- and Trans-Acting Elements Regulate the Mouse Psmb9 Meiotic Recombination Hotspot.
Baudat, F., de Massy, B
Characterization of Spo11-dependent and independent phospho-H2AX foci during meiotic prophase I in the male mouse
Chicheportiche A, Bernardino-Sgherri J, de Massy B, Dutrillaux B.
Playing hide and seek with mammalian meiotic crossover hotspots.
Buard, J., De Massy, B.
A Fast and Specific Alignment Method for Minisatellite Maps
Bérard S., Buard J. et E. Rivals.
Oligomerization of EDEN-BP is required for specific mRNA deadenylation and binding.
Cosson, B., Gautier-Courteille, C., Maniey, D., Ait-Ahmed, O., Lesimple, M., Osborne, H.B., Paillard, L.
Male cell microchimerism in normal and diseased female livers from fetal life to adulthood
Guettier, C., Sebagh, M., Buard, J., Feneux, D., Ortin-Serrano, M., Gigou, M., Tricottet, V., Reynes, M., Samuel, D., Feray, C.
Manipulating multiple sequence alignments via MaM and WebMaM
Alkan, C., Tuzun, E., Buard, J., Lethiec, F., Eichler, EE., Bailey JA., Sahinalp, SC.
Crossover and noncrossover pathways in mouse meiosis.
Guillon, H., Baudat, F., Grey, C., Liskay, R.M. and de Massy, B
The regulation of competence to replicate in meiosis by Cdc6 is conserved during evolution.
Lemaitre, JM., Bocquet, S., Terret, ME., Namdar, M., Ait-Ahmed, O., Kearsey, S., Verlhac, MH., and Méchali, M.
+
Réplication et Dynamique du Génome
The Drosophila Bruno paralogue Bru-3 specifically binds the EDEN translational repression element.
Delaunay J, Le Mée G, Ezzeddine N, Labesse G, Terzian C, Capri M, Aït-Ahmed O.
Distribution of meiotic recombination sites
de Massy, B.
Recombination across the centromere of disjoined and non-disjoined chromosomes 21
Laurent, A. M., Li, M., Sherman, S., Roizes, G., Buard, J.,
An initiation site for meiotic crossing-over and gene conversion in the mouse
Guillon H. and de Massy B.
Evolutionary fate of an unstable human minisatellite deduced from sperm-mutation spectra of individual alleles.
Buard J., Brenner C., Jeffreys A.J.
Instability of the human minisatellite CEB1 in rad27Delta and dna2-1 replication-deficient yeast cells.
Lopes J., Debrauwere H., Buard J., Nicolas A.
EDEN-dependent translational repression of maternal mRNAs is conserved between Xenopus and Drosophila
Ezzeddine, N., Paillard, L., Capri, M., Maniey, D., Bassez, T., Aït-Ahmed, O. and Osborne, H.B.
Influence of allele lineage on the role of the insulin minisatellite in susceptibility to type 1 diabetes.
Stead JD, Buard J, Todd JA, Jeffreys AJ.
Mécanisme d’instabilité des minisatellites.
Debrauwere H., Nicolas A., Vergnaud G., Buard J., Tessier J. et Aubert D.
Meiotic recombination and flanking marker exchange at the highly unstable human minisatellite CEB1 (D2S90)
Buard, J., Shone, A.C. and Jeffreys, A.J.
Somatic versus germline mutation processes at minisatellite CEB1 (D2S90) in humans and transgenic mice
Buard J., Collick A., Brown J. and Jeffreys, A.J.
Identification and characterization of an Spo11 homolog in the mouse
Metzler-Guillemain, C. et de Massy B.
Meiotic instability of human minisatellite CEB1 in yeast requires DNA double-strand breaks.
Debrauwere H, Buard J, Tessier J, Aubert D, Vergnaud G, Nicolas A.
The essential role of yeast topoisomerase III in meiosis depends on recombination.
Gangloff, S., De Massy, B., Lane, A., Rothstein, R. and Fabre, F.
A sequence based computational identification of Drosophila developmentally regulated TATA-less NA polymerase II promoter and its experimental validation.
Santoni, M.J., Aït-Ahmed, O. and Marilley, M.
Mitotic recombination and localized DNA double-strand breaks are induced after 8-methoxy psoralen and UVA irradiation in Saccharomyces cerevisia.
Dardhalon, M., De Massy, B., Nicolas, A. and Averbeck, D.
Implication of a 5'coding sequence in targeting maternal mRNA to the Drosophila oocyte.
Capri, M., Santoni, M.J., Thomas-Delaage, M. and Aït-Ahmed, O.
Thèses et hdr
La recombinaison méiotique dans le contexte de l’organisation des chromosomes chez la souris 11/03/2022
Soutenue par Mathilde Biot le 11/03/2022 sous la direction de Bernard De Massy
HDR 16/07/2021
 HDR “Control of the initiation of meiotic recombination in mouse”
HDR “Control of the initiation of meiotic recombination in mouse”
Par Corinne Grey le 26/05/2021
Propriétés biochimiques de la Topoisomérase VI d’Ectocarpus siliculosus et ses facteurs accessoires potentiels 30/03/2020
Soutenue par Julia Brinkmeier le 30-03-2020
Propriétés biochimiques et régulation du complexe TopoVI-like responsable de l'initiation de la recombinaison méiotique. 29/11/2018
Soutenue par Alexandre Nore le 29-11-2018
Évolution de la recombinaison Méiotique : variation et fonction du gène Prdm9 chez la souris 25/11/2016
Soutenue par Denis Dunoyer de Segonzac le 25-11-2016
Rôle de l'activité méthyltransférase de la protéine PRDM9 dans la recombinaison méiotique chez la souris 11/12/2015
Soutenue par Boubou Diagouraga le 15-12-2015
Initiation de la recombinaison méiotique chez la souris : recherche de partenaires de la protéine PRDM9 11/12/2015
Soutenue par Yukiko Imai le 11/12/2015